Top Useful Data analysis Formulas | Excel Formulas
Top Most Useful Data analysis Formulas | Excel Formula & Get free lessons & ATS CV
1. INDEX MATCH
Formula: =INDEX(C3:E9,MATCH(B13,C3:C9,0),MATCH(B14,C3:E3,0))
This is an advanced alternative to the VLOOKUP or HLOOKUP formulas (which have several drawbacks and limitations). INDEX MATCH is a powerful combination of Excel formulas that will take your financial analysis and financial modeling to the next level.
INDEX returns the value of a cell in a table based on the column and row number.
MATCH returns the position of a cell in a row or column.
Enroll for best Data Analysis Courses. Click here
2. IF combined with AND / OR
Formula: =IF(AND(C2>=C4,C2<=C5),C6,C7)
Anyone who’s spent a great deal of time doing various types of financial models knows that nested IF formulas can be a nightmare. Combining IF with the AND or the OR function can be a great way to keep formulas easier to audit and easier for other users to understand. In the example below, you will see how we used the individual functions in combination to create a more advanced formula.
For a detailed how to use IF enroll now.
3. XNPV and XIRR
Formula: =XNPV(discount rate, cash flows, dates)
If you’re an analyst working in investment banking, equity research, financial planning & analysis (FP&A), or any other area of corporate finance that requires discounting cash flows, then these formulas are a lifesaver!
Simply put, XNPV and XIRR allow you to apply specific dates to each individual cash flow that’s being discounted. The problem with Excel’s basic NPV and IRR formulas is that they assume the time periods between cash flow are equal. Routinely, as an analyst, you’ll have situations where cash flows are not timed evenly, and this formula is how you fix that.
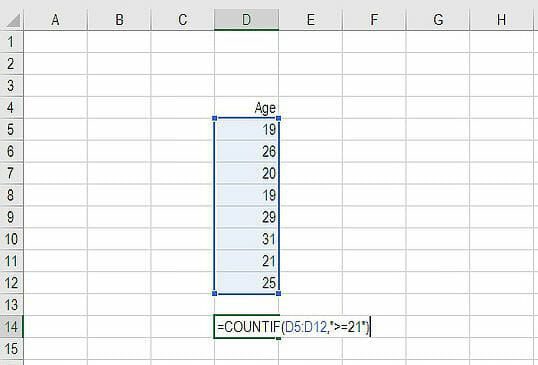
4. SUMIF and COUNTIF
Formula: =COUNTIF(D5:D12,”>=21″)
These two advanced formulas are great uses of conditional functions. SUMIF adds all cells that meet certain criteria, and COUNTIF counts all cells that meet certain criteria. For example, imagine you want to count all cells that are greater than or equal to 21 (the legal drinking age in the U.S.) to find out how many bottles of champagne you need for a client event. You can use COUNTIF as an advanced solution, as shown in the screenshot below.
To know more enroll in our Data Analysis Courses. Click here
5. PMT and IPMT
Formula: =PMT(interest rate, # of periods, present value)
If you work in commercial banking, real estate, FP&A or any financial analyst position that deals with debt schedules, you’ll want to understand these two detailed formulas.
The PMT formula gives you the value of equal payments over the life of a loan. You can use it in conjunction with IPMT (which tells you the interest payments for the same type of loan), then separate principal and interest payments.
Here is an example of how to use the PMT function to get the monthly mortgage payment for a $1 million mortgage at 5% for 30 years.
6. LEN and TRIM
Formulas: =LEN(text) and =TRIM(text)
The above formulas are a little less common, but certainly very sophisticated ones. They are great for financial analysts who need to organize and manipulate large amounts of data. Unfortunately, the data we get is not always perfectly organized and sometimes, there can be issues like extra spaces at the beginning or end of cells.
The LEN formula returns a given text string as the number of characters, which is useful when you want to count how many characters there are in some text.
In the example below, you can see how the TRIM formula cleans up the Excel data.
Enroll for best Data Analysis Courses. Click here
7. CONCATENATE
Formula: =A1&” more text”
Concatenate is not really a function on its own – it’s just an innovative way of joining information from different cells and making worksheets more dynamic. This is a very powerful tool for financial analysts performing financial modeling (see our free financial modeling guide to learn more).
In the example below, you can see how the text “New York” plus “, “ is joined with “NY” to create “New York, NY”. This allows you to create dynamic headers and labels in worksheets. Now, instead of updating cell B8 directly, you can update cells B2 and D2 independently. With a large data set, this is a valuable skill to have at your disposal.
Enroll for best Data Analysis Courses. Click here
10. CELL, LEFT, MID and RIGHT functions
These advanced Excel functions can be combined to create some very advanced and complex formulas to use. The CELL function can return a variety of information about the contents of a cell (such as its name, location, row, column, and more). The LEFT function can return text from the beginning of a cell (left to right), MID returns text from any start point of the cell (left to right), and RIGHT returns text from the end of the cell (right to left).
Enroll for best Data Analysis Courses. Click here
Download coupons, free knowledge library & Free ATS CV